In elementary algebra, root rationalisation is a process by which radicals in the denominator of an algebraic fraction are eliminated.
Rationalisation of the denominator:
Subject to x, y > 0,
1/(√x - √y) = (√x + √y)/{(√x - √y)(√x + √y)} = (√x + √y)/(x-y)
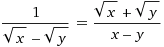
Rationalisation of the numerator:
Subject to x, y > 0,
√x - √y = (√x - √y)(√x + √y)/(√x + √y) = (x-y)/(√x + √y)
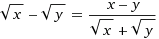
Double rationalisation:
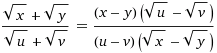

Write a comment