<what is Poisson distribution?>
Poisson distribution can be derived from binomial distribution.
<what is binomial distribution?>
preparing n boxes and each box can take p or q below.
(p/q)(p/q)(p/q)・・・(p/q)
all combinations of p and q are
(p+q)^n = ΣnCx p^x q^(n-x)
here, when p+q = 1, nCx p^x q^(n-x) is probability density.
let nCx p^x q^(n-x) be f(x).
f(x) is binomial distribution.
<properties of binomial distribution>
the mean value of f(x) is μ = np.
the variance of f(x) σ^2 = npq = np(1-p).
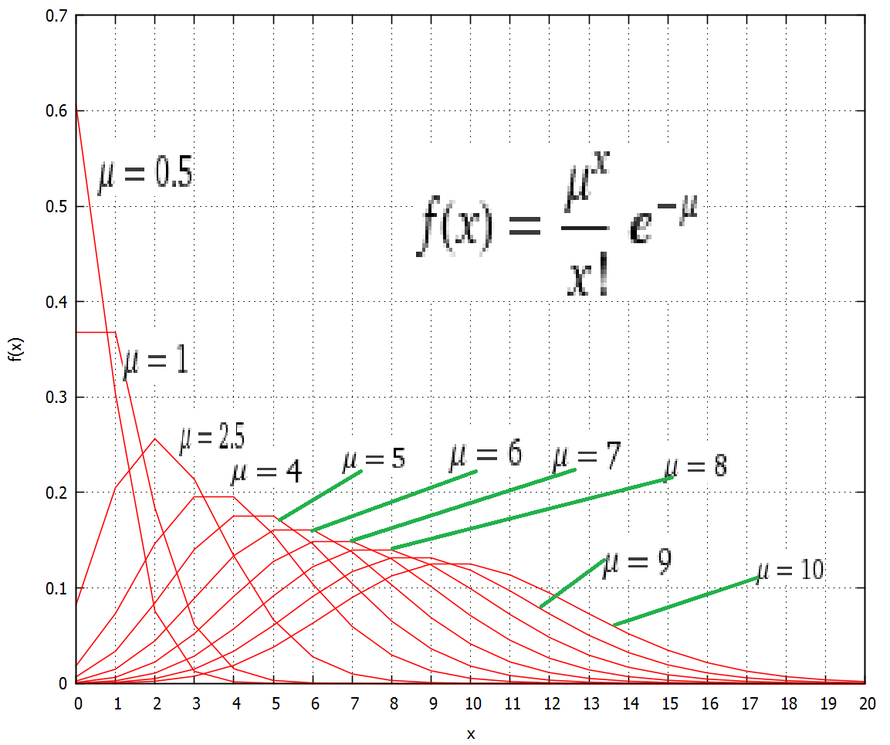
<Poisson distribution again>
n->∞, p->0 subject to np = μ = const.
nCx p^x q^(n-x) -> (μ^x e^(-μ))/x!
roughly speaking,
nCx -> 1/x!
p^x -> μ^x
q^(n-x) -> e^(-μ)
, which would help you remember the distribution.
<example of Poisson distribution>
radioisotope polonium 210 emits alpha particles 100%.
properties of it:
decay constant λ=3.4 * 10^(-6)[/min], μ=12/min.
then, what is the probability of 15/min?
n is so many, p(λ) is so small, μ=const.
so that 210Po should obeys Poisson distribution.
f(x) = 12^x e^(-12))/x!
therefore
f(15) = 7.24 * 10^(-2)

Write a comment